How to Take Notes From YouTube Videos Effectively
Learn how to make notes from YouTube videos effectively using timestamps, transcripts, and simple tools to turn video content into reusable notes.

Most of us hit play on a YouTube video, tell ourselves we will remember the good parts, and then move on with nothing written down. We have done that more times than we can count. The problem isn’t the video. It is how we watch it.
Taking notes from YouTube videos effectively means listening actively instead of watching passively, pausing and replaying key moments, and writing short notes linked to timestamps or transcript sections. When you summarize ideas in your own words and review notes after watching YouTube videos turn into usable study and reference material. Tools like Web Highlights make this easier by keeping notes tied to the exact part of the video.

Why YouTube Requires a Different Note-Taking Approach?
Taking notes from a YouTube video is not the same as taking notes from a book or article.
Videos are linear and time-based. Once something is said, it is gone unless you pause or rewind. That is where most people lose focus. This problem becomes even more noticeable with short-form video, where ideas move fast, and there is very little time to pause and reflect.
When you rewind again and again, your attention breaks. Many learners reach the end of a video with no structured notes, no timestamped notes, and no clear key takeaways. The result is low learning potential, even from good educational resources, training videos, or long-form video content.
This is why people struggle to make notes from YouTube video content. Watching feels easy, but turning spoken ideas into actionable notes, reference materials, or study materials needs a different approach than text-based note-taking.
Common Mistakes When Taking Notes From YouTube Videos
Most people don’t struggle because a YouTube video is confusing. The issue is how notes are taken while watching. Small habits make a big difference. Here are some common mistakes that you might be making:
- Trying to write everything word-for-word - This turns note-taking into transcription. You miss key information and end up with messy notes instead of clear action items.
- Not pausing the video - Letting the video run while writing leads to shallow notes. Pausing helps turn spoken ideas into structured notes you can reuse.
- Taking notes without timestamps - Notes without timestamps lose context. You can’t trace ideas back to the exact moment later.
- Relying on memory after watching - Memory fades fast. Without written notes, even strong learning material disappears within hours.
- Not revisiting notes - Notes that aren’t reviewed never become part of your searchable knowledge bases or long-term personal knowledge management system.
If you want to take notes from YouTube videos that actually help later, these habits have to change.
How To Prepare Before Taking Notes From A YouTube Video
Good notes start before the video even plays. Spending a few minutes on setup reduces rewinding and keeps attention steady. Use this simple checklist before starting any YouTube video.
1. Define the goal first
Be clear about why the video is being watched. Study, research papers, exam revision, or skill building all require different levels of detail and different types of structured notes.
2. Scan the description and chapters
Video descriptions and chapters show what topics are covered and in what order. This helps identify key information and avoids wasting time on sections that are not relevant.
3. Set the playback speed on purpose
Dense explanations benefit from a slower speed, while familiar topics can be watched faster. Adjusting speed improves focus and the overall learning experience.
4. Choose a note-taking method in advance
Decide whether to use outlines, timestamped notes, a mind map, or question-based notes. Picking a method early keeps notes consistent and easier to review later.
This small preparation step makes it easier to make notes from YouTube video content that actually turns into useful learning material.
Step-By-Step Process For Taking Notes From YouTube Videos
This step-by-step method works for lectures, training videos, tutorials, and long-form video content. It helps turn watching into usable notes instead of passive viewing.
1. Watch Actively, Not Passively
Treat the YouTube video like a live class, not background noise. Stay alert for examples, definitions, and explanations that carry key information. Active watching improves focus and learning potential.
2. Pause At Key Ideas
Pause whenever an idea sounds important or reusable. This is where most action items, concepts, or explanations appear. Pausing prevents overload and keeps notes accurate.
3. Write Short, Meaningful Notes
Avoid full sentences copied from the video. Write clear phrases or bullet points that explain the idea in simple words. This creates structured notes that are easier to review later.
4. Add Timestamps Or Transcript References
Always link notes to time markers or transcript sections. Timestamped notes preserve context and make it easy to revisit exact moments without scrubbing through the video.
5. Summarize Sections In Your Own Words
After a section ends, write a brief summary. This step turns raw notes into actionable notes and improves recall when using notes as study materials or reference materials.
Using this process consistently makes it easier to take notes from YouTube videos and store them inside searchable knowledge bases. Tools like Web Highlights support this workflow by allowing users to highlight transcripts, add notes, and keep everything connected to the original video. You can also generate quick AI summaries that can be combined with your notes.
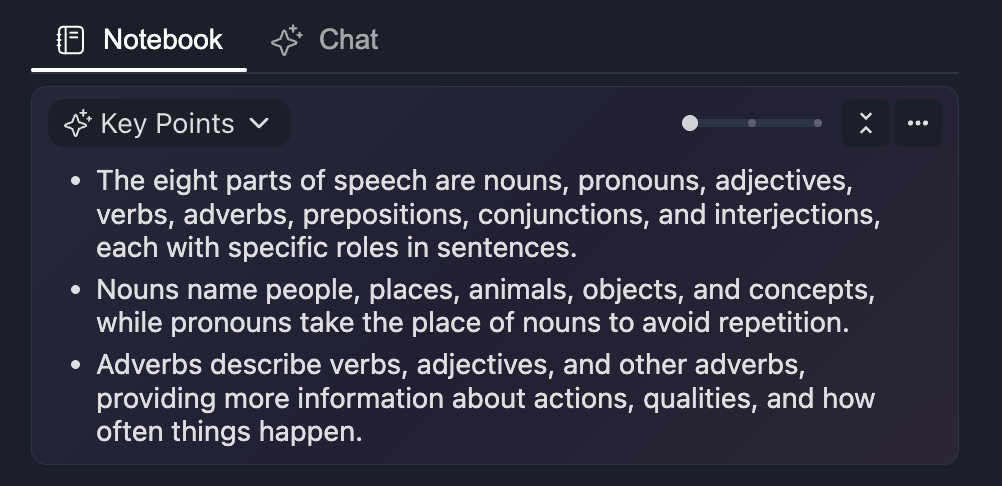
Manual Vs Digital Note-Taking For YouTube Videos
There’s no single right way to make notes from YouTube videos. It really comes down to how fast notes are needed, how accurate they should be, and how often they’ll be reviewed later. The question is: do the notes need to be revisited, or are they just for the moment?
Notebook + Timestamps
Writing notes by hand works well for focused watching and simple ideas. Timestamps can be written next to key points, but finding the exact moment again takes time. For long video content, this method becomes slower and harder to reuse.
Google Docs Or Notion
Typing notes in Google Docs or Notion is faster than handwriting and easier to organize as structured notes. Timestamps are added manually, which means frequent pausing. Reviewing often involves switching back and forth between the video and the document.
Browser-Based Highlighting On Transcripts
Highlighting directly on transcripts keeps notes tied to the source. There’s less rewinding, better transcription accuracy, and lower review effort. Notes stay linked to exact sections of the YouTube video, which makes revisiting ideas much easier.
If the goal is quick notes, almost any method works. But if notes are meant to become learning material or reference materials, staying connected to the video matters more than most people expect.
Web Highlights supports transcript-based notes by letting users highlight, tag, and export notes. This makes it easier to turn video content into reusable learning material without extra steps.
Why Timestamps And Transcripts Improve YouTube Notes
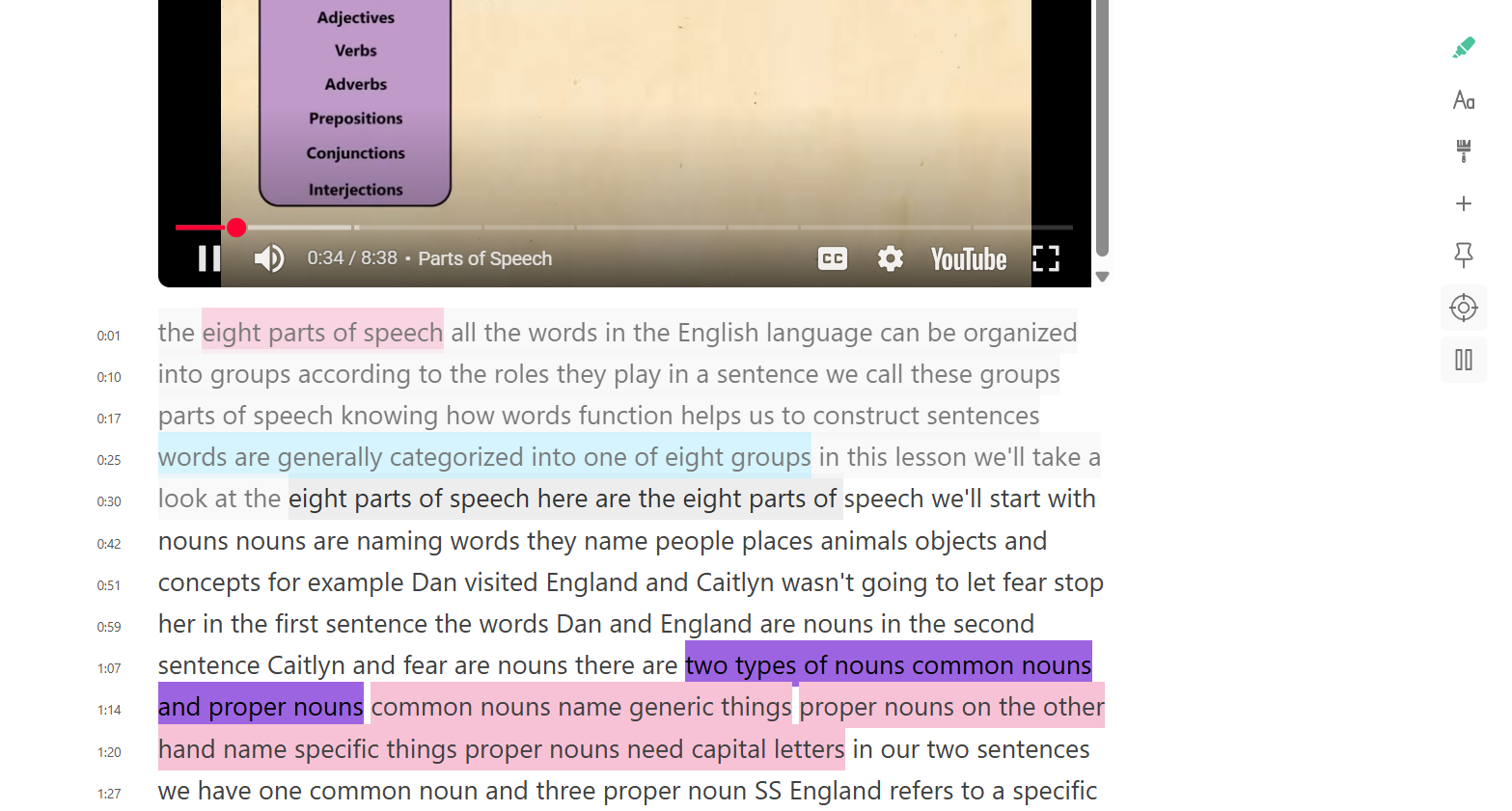
Timestamps and transcripts solve the biggest problem with video notes: lost context. When notes are tied to time and text, they stay useful long after the video ends.
Timestamps preserve context
A note linked to a specific moment shows exactly where an idea appears. Timestamped notes make it easy to jump back to the right section without guessing or scanning the whole YouTube video.
Transcripts make reviewing faster
Reading is faster than rewatching, especially when AI help is used to surface transcripts quickly. Transcripts turn spoken video content into searchable text, which helps find key information, quotes, and definitions in seconds.
Transcript-based notes reduce rewinding
When notes are taken directly from transcript sections, there is less need to pause and rewind. This keeps focus steady and improves the overall learning experience.
The AI transcript reader in Web Highlights supports this workflow by allowing users to read YouTube transcripts online, highlight exact lines, add notes, and keep everything linked to the original video. This makes it easier to take notes from YouTube videos and reuse them later as study materials or reference materials.
Best Note-Taking Methods For YouTube Videos
Not every YouTube video needs the same type of notes. The method should match how the video explains ideas and how the notes will be used later.
1. Outline Method
The outline method works well for lectures, tutorials, and longer educational resources. Notes follow the video's order, using clear headings and subpoints. This helps keep ideas organized and easier to review later.
2. Cornell-Style Notes (Adapted For Video)
Cornell-style notes are useful for exam preparation and revision. When used with videos, timestamps replace page numbers. Key points go on one side, questions or cues on the other, followed by a short summary for recall.
3. Question-Based Notes
Question-based notes suit interviews, panel discussions, and explainer videos. Writing notes as questions keeps attention focused and turns them into quick review material for study materials.
4. Concept Mapping
Concept mapping works well for complex or connected topics. A mind map helps show how ideas relate across the video content, instead of listing points in isolation.
5. TL;DR
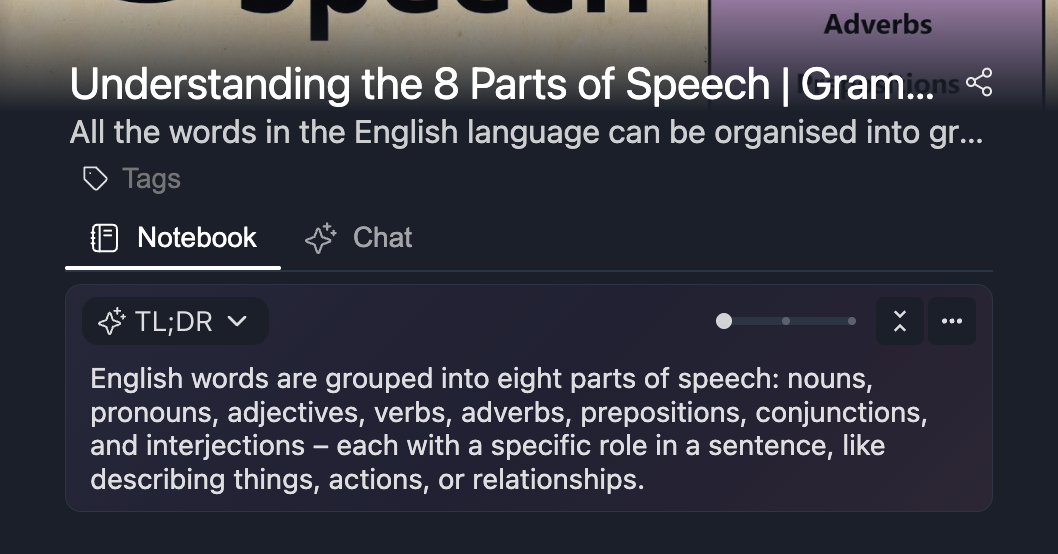
Lectures work best with outlines. Exam revision fits Cornell-style notes. Interviews benefit from question-based notes. Complex topics are easier to understand with concept mapping.
Web Highlights also offers AI summaries for YouTube videos in formats like TL;DR and bullet points. These summaries can be used as a starting reference, while manual notes remain tied to transcripts and timestamps for accuracy when you take notes from YouTube videos.
Taking Notes From YouTube Lectures As A Student
Students use YouTube video lectures in many ways, from full online classes to quick revision before exams. The way notes are taken from videos is different from how notes are taken from textbooks.
For online classes, video notes need more structure. Spoken explanations move quickly, so timestamped notes help track where definitions, examples, and explanations appear. This makes it easier to return to the exact moment later without rewatching the full lecture.
For exam revision, students often focus on key takeaways and formulas rather than full explanations. Short, structured notes work better than long paragraphs, especially when notes are reused as study materials.
For concept reinforcement, videos explain ideas in a more conversational way than textbooks. Notes should capture examples and explanations in simple language, not copied sentences. This improves understanding and long-term recall.
Unlike textbook notes, video notes depend on time and context. Linking notes to transcripts or timestamps helps turn video content into reliable learning material that can be reviewed, searched, and reused later when students take notes from YouTube videos.
Using YouTube Videos For Research Note-Taking
Researchers use YouTube video content very differently from casual viewers. In many cases, they treat videos as video data that needs the same care as written sources. Talks, interviews, and method explainers often support arguments, citations, or background sections in research papers, so notes need to be precise.
Common research use cases include:
- Recorded talks and panels where multiple speakers share different viewpoints
- Expert interviews that include definitions, opinions, or quoted insights
- Methodology explanations that walk through processes step by step
When taking notes from these videos, three things matter most:
Traceability - Every important point should link back to an exact moment in the video. Timestamped notes make it clear where each idea came from.
Accurate Referencing - Research notes need correct wording and context. Notes tied to transcript lines reduce mistakes and improve transcription accuracy.
Revisiting Exact Moments Later - Being able to jump back to a specific second avoids rewatching full videos and protects focus.
This approach turns video content into dependable reference materials, not loose notes that rely on memory.
Tools That Help You Take Notes From YouTube Videos
Different tools support different ways to make notes from YouTube videos. The right choice depends on how easily notes can be reviewed, reused, and shared later.
1. Web Highlights
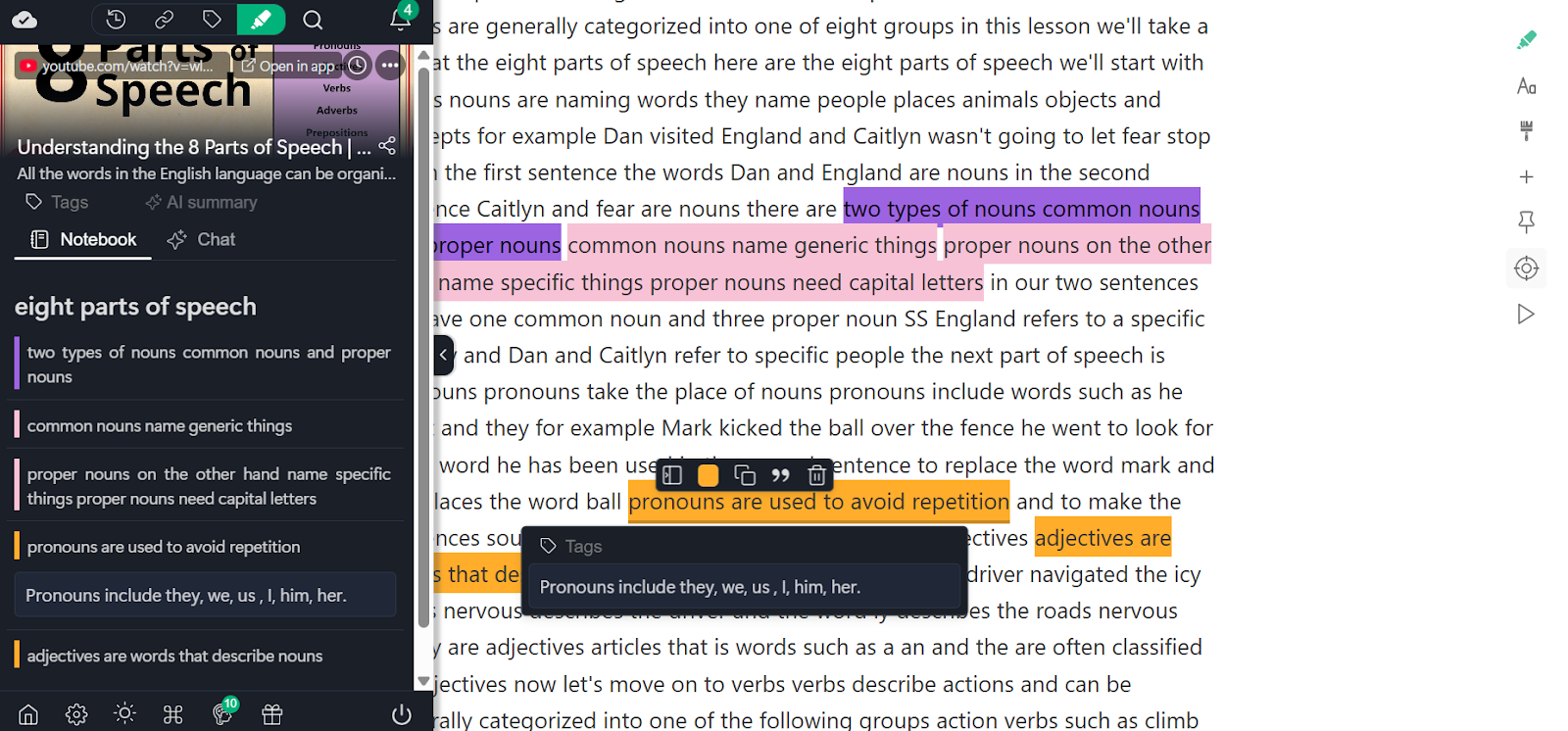
Web Highlights allows users to highlight YouTube video transcripts instead of copying text into another app. Notes stay linked to exact transcript sections and timestamps, with tags for organization. Highlights and notes can be exported in multiple export options, making it easy to reuse them as study materials, reference materials, or for research papers.
2. Notion
Notion supports structured notes and flexible layouts. Timestamps are usually added manually while watching the video. Notes can be organized and exported, but the process requires switching between the video and the document.
3. Google Docs
Google Docs works for basic timestamped notes written during playback. Notes can be shared or exported, but there is no direct link to transcripts or video sections, which limits long-term reuse.
Exporting notes and highlights makes it easier to turn video content into reusable learning material instead of notes that stay locked inside one tool.
How To Review And Remember Notes From YouTube Videos
Taking notes is only half the work. The real value comes from how those notes are reviewed and reused. Without review, even good notes from a YouTube video fade quickly.
Revisit notes within 24 hours - A quick review soon after watching helps lock in key information. This small step keeps notes from turning into forgotten text.
Rewrite notes into short summaries - Turning raw notes into brief summaries helps clarify ideas. These summaries work well as study materials, quick reference materials, or even outlines for future blog posts.
Group-related video notes together - Notes from multiple videos often cover similar ideas. Grouping them builds structured notes and supports long-term personal knowledge management.
Connect notes across videos - Linking ideas from different video content creates context. Over time, notes evolve into searchable knowledge bases rather than isolated points.
Reviewing this way helps take notes from YouTube videos that actually support learning, exam revision, and deeper understanding.
Taking YouTube Notes With Web Highlights
If notes are meant to be reused later, how they are captured matters. Copying text into another app often breaks context and slows things down.
With Web Highlights, notes are taken directly from YouTube video transcripts using a Chrome extension that runs in the browser. Instead of copying lines manually, users highlight the exact text where an idea appears and add notes alongside it. This keeps notes connected to the precise video section where the key information was explained.
Tags make it easier to organize notes across multiple videos, courses, or topics. This helps when working with large amounts of learning material, training videos, or academic video content. Notes and highlights can also be exported using available export options, making them useful for study materials, research papers, or long-term personal knowledge management.
For anyone who wants to take notes from YouTube videos without losing context, keeping notes tied to transcripts reduces the need to rewind and makes review simpler later.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is It Better To Pause or Watch First, Then Take Notes?
Pausing works better for most people. Watching first often leads to forgotten details. Pausing at key moments helps capture key information, add timestamped notes, and turn a YouTube video into clear, usable notes, rather than relying on memory.
2. How Long Should YouTube Notes be?
YouTube notes should be short and focused. Aim for bullet points, definitions, and examples rather than full sentences. Good notes highlight key takeaways and action items without copying everything said in the video.
3. Do YouTube Transcripts Replace Note-Taking?
No. Transcripts show what was said, but they don’t explain what matters. Notes add meaning by selecting important points, adding context, and organizing ideas. Transcripts support note-taking, but they don’t replace it.
4. Are YouTube Notes Useful for Exams or Research?
Yes. When notes include timestamps and a clear structure, they work well for exam revision and research papers. Notes linked to exact video moments make it easier to verify ideas and revisit explanations later.
5. Can YouTube Notes be Reused Later?
Yes, if notes are organized and searchable. Tagged and exported notes can be reused as study materials, reference materials, or part of a personal knowledge management system across multiple topics and videos.
6. What is The Easiest Way to Keep YouTube Notes Organized?
Using transcript-based notes helps keep everything connected. Tools like Web Highlights allow notes to stay linked to video sections, be tagged by topic, and be exported for reuse, reducing review effort later.


